ESG Investing: Aligning Values with Returns

Tanya Iyer
ESG Research Analyst

In recent years, ESG investing—short for Environmental, Social, and Governance investing—has moved from a niche interest to a mainstream financial strategy embraced by institutions and retail investors alike. It reflects a growing awareness that long-term value creation is not just about profits, but also about the sustainability and ethical impact of the companies we invest in.
What Exactly is ESG Investing?
ESG investing evaluates companies based on their environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and governance structures. This includes how a company manages its carbon footprint, treats employees and communities, and ensures transparency in executive decisions. These factors are increasingly being linked to financial performance, making ESG a relevant filter for portfolio construction.
Environmental criteria examine how a company performs as a steward of nature. Social criteria look at how it manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates. Governance deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights.
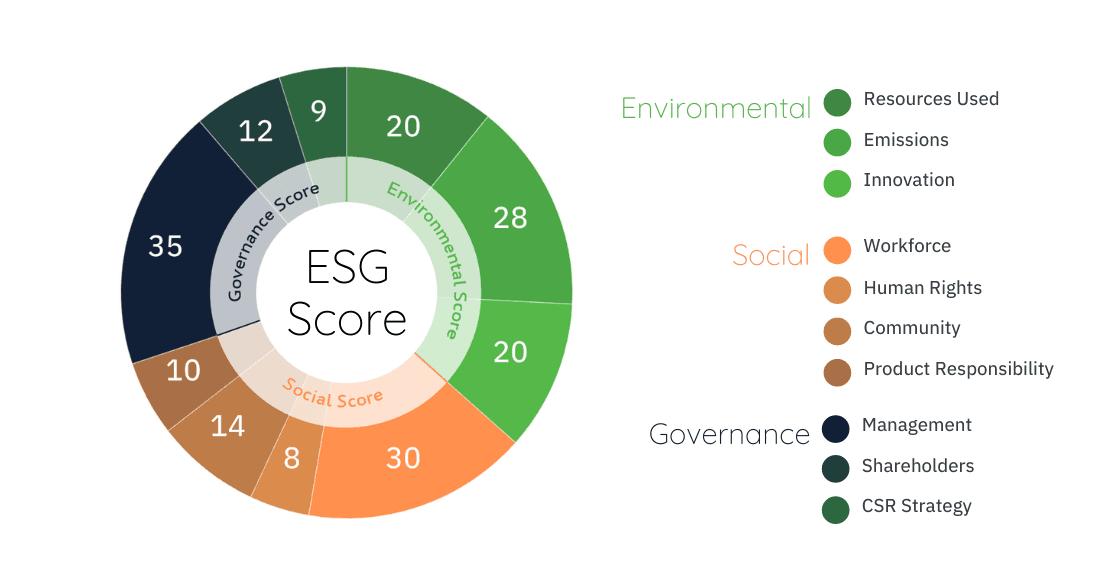
Why ESG Matters More Than Ever
The urgency of climate change, the social upheavals around inequality, and a wave of corporate scandals have all contributed to a rethinking of what constitutes responsible investing. Investors are realizing that ESG issues can have a direct impact on a company’s long-term viability and financial performance. For instance, companies with poor environmental records may face fines or stricter regulations, while those with poor labor practices may suffer from strikes, boycotts, or reputational damage.
Companies that score high on ESG metrics tend to outperform peers over the long term, both in returns and resilience.
ESG metrics are now being integrated into mainstream investment tools. Major fund managers, including BlackRock and Vanguard, have committed to ESG screening, and over $30 trillion in global assets are now managed with some form of ESG consideration.
How to Start with ESG Investing
There are various ways to incorporate ESG principles into an investment strategy. One can invest in mutual funds or ETFs that specifically screen for ESG criteria. Another approach is to directly buy shares of companies with strong ESG performance. Many financial platforms now offer ESG scores for individual stocks to help guide investment decisions.
- Use ESG-focused mutual funds or ETFs
- Check ESG scores via financial platforms like Morningstar or MSCI
- Engage in shareholder activism by voting on corporate issues
- Avoid investing in companies or industries with negative ESG profiles
Challenges and Criticism
Despite its growing popularity, ESG investing is not without controversy. Critics argue that ESG metrics are inconsistent, lack standardized reporting, and sometimes serve as mere marketing tools for companies. Additionally, some fear that ESG-focused funds may underperform traditional funds due to limited investment options. However, recent research suggests that well-constructed ESG portfolios can deliver competitive—if not superior—returns.
The Future of ESG
As regulators push for more transparency and standardization, ESG investing is expected to become more robust and reliable. Innovations like green bonds, ESG derivatives, and AI-driven ESG analytics will likely deepen the integration of ethical considerations in the investment process.
In summary, ESG investing represents a fundamental shift in how we define investment success. It acknowledges that long-term prosperity must be shared, sustainable, and socially conscious.
Share this article
About the author
Tanya is a Mumbai-based finance expert with a focus on sustainable investing and impact measurement.